
The Ultimate Guide to Comparing Industrial Cooler Options
Introduction to Industrial Coolers
Industrial coolers are specialized refrigeration systems engineered to maintain precise temperatures in commercial, industrial, and institutional settings. From protecting perishable food to keeping sensitive electronics within safe operating limits, robust cooling technology underpins countless modern processes.
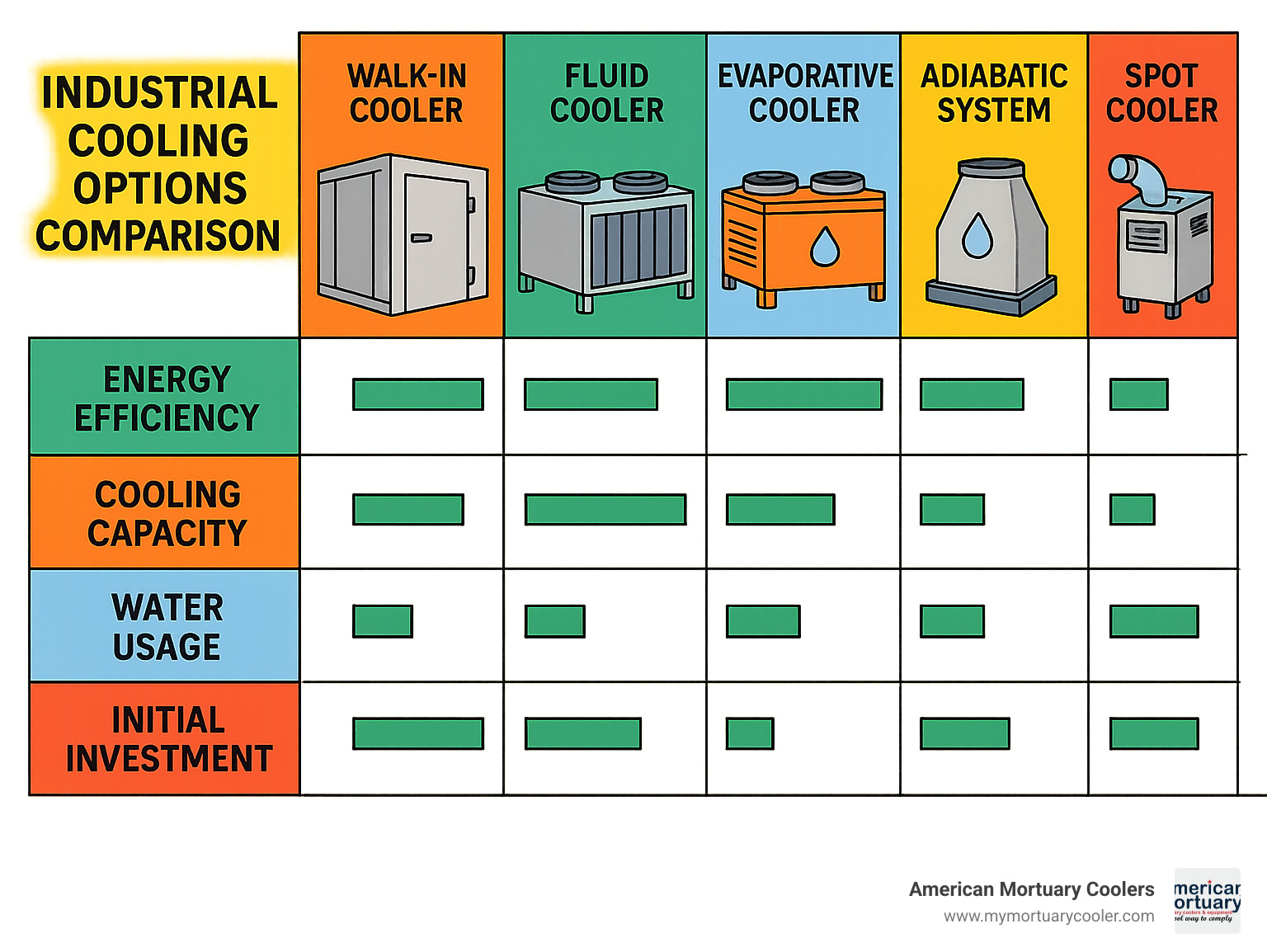
Quick Overview of Industrial Cooler Types
| Type | Primary Use | Key Benefit | Typical Industries |
|---|---|---|---|
| Walk-in Coolers | Large-scale cold storage | Up to 1,600 sq ft of storage space | Food service, warehousing, mortuary |
| Fluid Coolers | Process cooling | Closed-loop efficiency | Manufacturing, power generation |
| Evaporative Coolers | Large-area comfort/process cooling | Energy savings up to 70 % vs. mechanical refrigeration | Industrial facilities, data centers |
| Adiabatic Coolers | Heat rejection | Water and energy efficiency | Power plants, process cooling |
| Spot Coolers | Targeted cooling | Mobility and flexibility | Manufacturing, event cooling |
Selecting the right cooling technology can dramatically influence operating costs, product quality, and overall reliability. Whether you manage a manufacturing line, a commercial kitchen, or a funeral home, understanding the strengths of each option helps you make informed, cost-effective decisions.
Tip: Terminology can vary between industries. If you need a refresher on common phrases like “commercial cooling” or “outdoor freezer,” check the linked resources later in this guide. They provide context without interrupting your selection process.
Understanding Industrial Coolers: Types, Applications & How They Work
Industrial coolers rely on three main heat transfer processes: conduction (direct contact), convection (air/liquid carrying heat away), and phase change (cooling through evaporation). These principles, applied at industrial scale, keep our modern world running cool.
Main Types of Industrial Coolers
Air-cooled systems are straightforward workhorses with large external fans. They're simpler to install since they don't need water connections, making them perfect for places with limited water access.
Water-cooled systems are efficiency champions using water's excellent heat-carrying capacity to cool more effectively than air, especially in high temperatures. While they require water infrastructure, their energy savings often justify the extra setup.
Evaporative coolers work well in hot, dry regions, slashing energy costs by up to 70% compared to traditional refrigeration by using evaporation. When water evaporates, it takes heat with it, creating a natural cooling effect.
Dry coolers offer a smart solution for environmentally-conscious operations. These closed-loop systems transfer heat without consuming water, using fans to push air across finned coils containing process fluid.
Chillers maintain exact temperatures below the surrounding environment, making them essential for manufacturing processes where even small temperature variations can ruin products.
Spot coolers like the LSX Series provide targeted cooling for specific areas without wasting energy cooling unnecessary space.
Oil coolers prevent hydraulic and lubricating oils from breaking down under heat, extending equipment life and preventing costly breakdowns.
Where Industrial Coolers Are Used
Industrial coolers touch almost every product we use daily. In food and beverage operations, walk-in coolers provide up to 1,600 square feet of cold storage for restaurant ingredients and supermarket produce.
The pharmaceutical industry depends on precise cooling to maintain medication potency and research integrity. Even small temperature fluctuations can render expensive medicines ineffective.
In manufacturing facilities, cooling systems remove excess heat, protecting equipment from premature wear while ensuring consistent product quality.
Data centers generate enormous heat from servers working 24/7. Specialized cooling systems prevent these critical systems from overheating and crashing.
Breweries and distilleries rely on cooling at multiple production stages – from chilling wort after boiling to maintaining perfect fermentation temperatures.
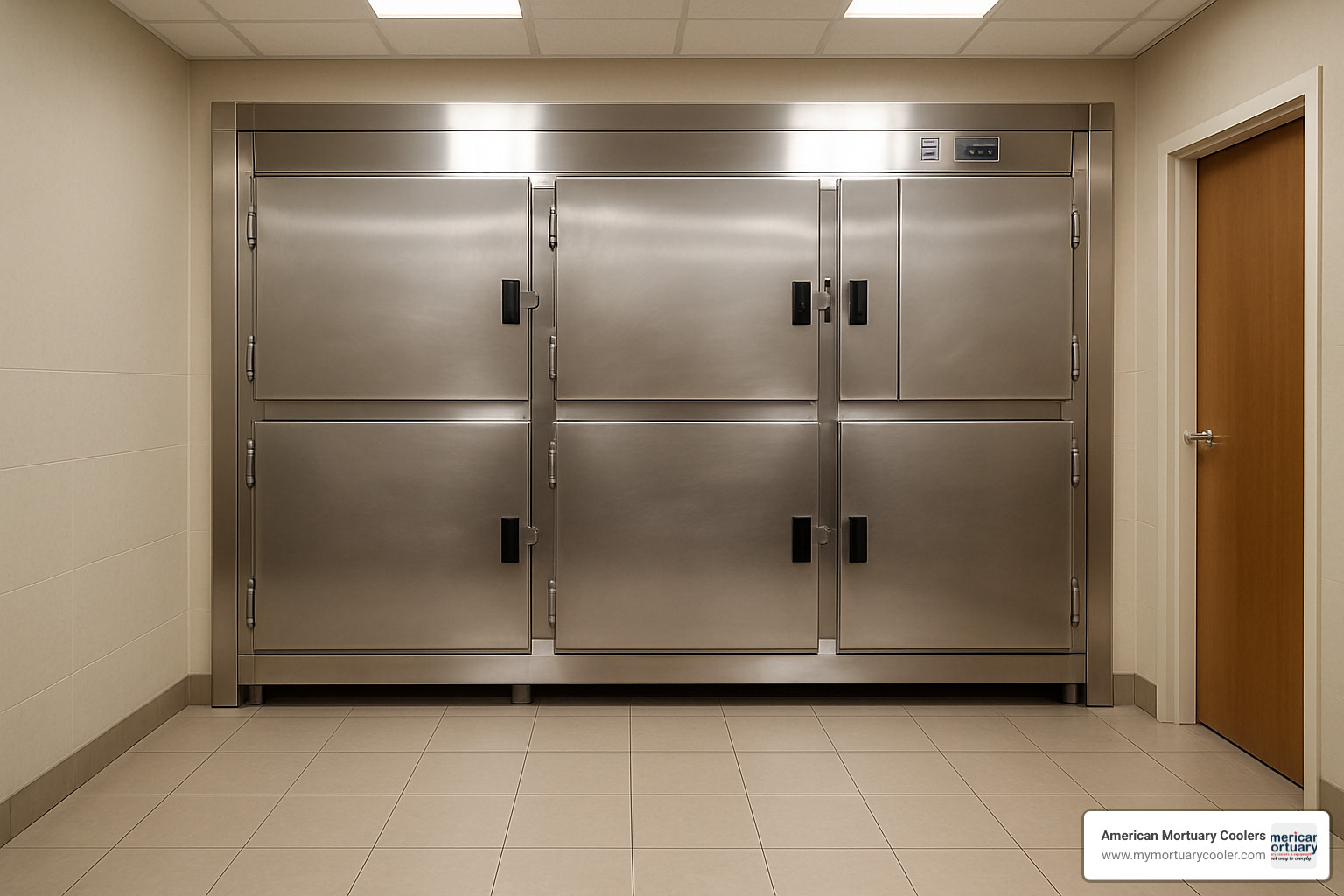

In funeral homes and mortuaries, specialized cooling systems provide dignified care for the deceased before services. At American Mortuary Coolers, we've developed expertise in this sensitive application, creating systems that balance technical performance with the respectful environment funeral directors need.
For those interested in specialized refrigeration combinations, our guide to walk-in fridge combos explores how these versatile systems can improve operational efficiency while meeting specific cooling needs.
Comparing Industrial Coolers Technologies & Performance
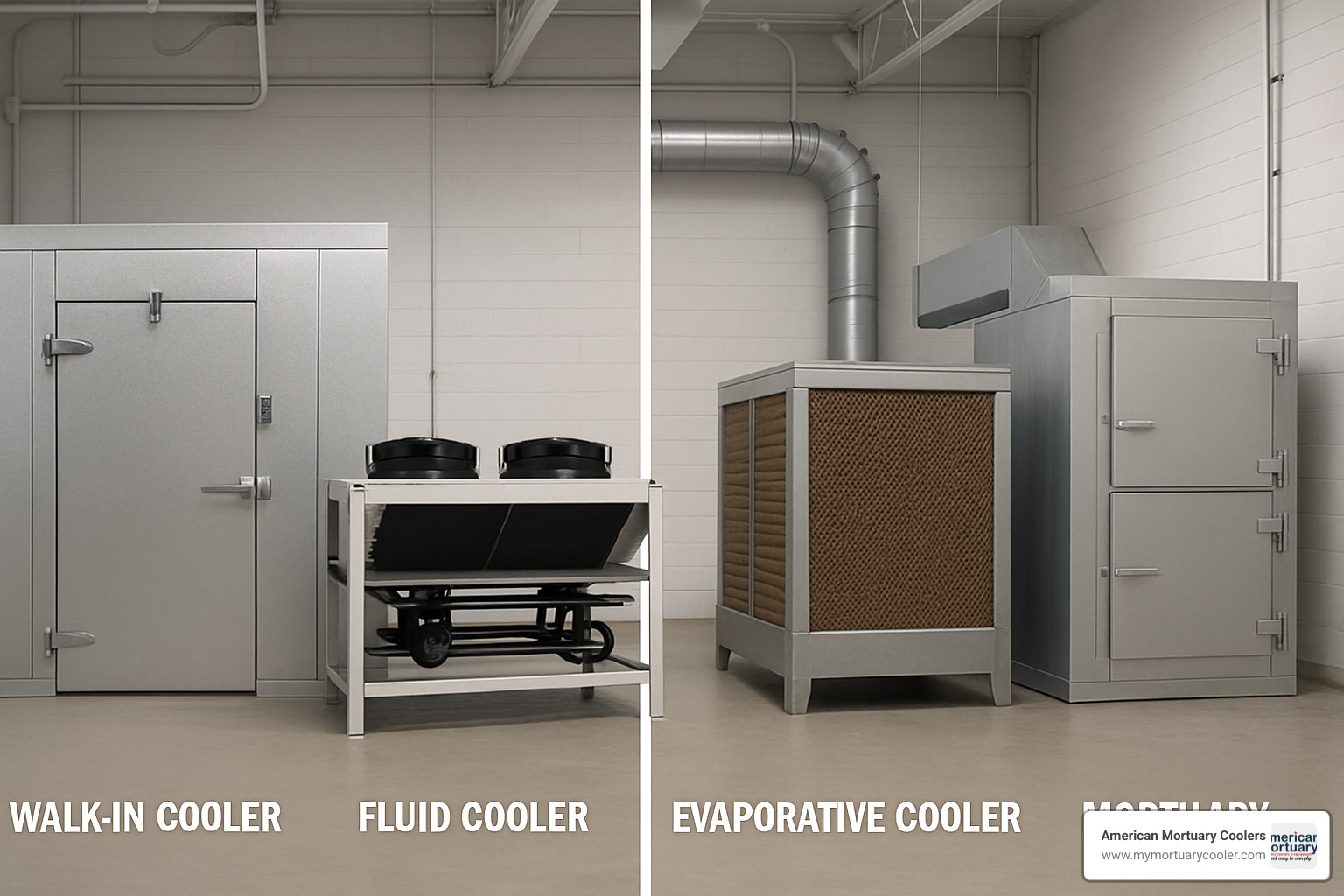

Advantages & Disadvantages of Key Industrial Cooler Types
Air-Cooled Systems
Air-cooled industrial coolers don't need water to operate and have simpler maintenance schedules. They're ideal for locations where water is scarce or expensive.
The downside? They work harder and louder in high temperatures, increasing energy bills. They also require more space than water-cooled systems for the same cooling capacity.
Water-Cooled Systems
Water-cooled industrial coolers maintain efficiency even when outside temperatures climb, making them ideal for hot climates. They operate more quietly without roaring fans.
However, they need a steady supply of quality water and regular treatment to prevent scale buildup. Installation costs more upfront, and freezing climates require pipe protection.
Evaporative Coolers
Evaporative industrial coolers can reduce cooling energy costs by up to 70% in dry climates. They also provide ventilation, bringing fresh air into spaces.
However, they lose effectiveness in humid environments and require water and regular maintenance to prevent mineral buildup. They're not ideal for precise temperature control applications.
Adiabatic Coolers
Adiabatic industrial coolers use water only when needed to pre-cool air. This hybrid approach saves water compared to cooling towers while maintaining efficiency. They have reduced risk of Legionella since they don't create aerosols.
They cost more initially than simple dry coolers and have more complex controls, requiring both water and electrical connections.
Spot Coolers
Spot industrial coolers provide targeted cooling where needed. They're mobile, flexible, and ready to deploy wherever heat causes problems. The Dry Coolers LSX Series Spot Cooler exemplifies this technology.
These systems aren't designed for cooling entire buildings and typically cost more per ton of cooling capacity than centralized systems.
How Industrial Coolers Impact Product Quality & Process Reliability
Temperature Stability is crucial in sensitive industries. In pharmaceutical manufacturing, even small fluctuations can render medications useless. Quality industrial coolers maintain consistent temperatures for reliable products.
Humidity Control varies by system type. Evaporative systems naturally increase humidity—perfect for wood processing but potentially problematic for electronics manufacturing.
Uptime & Reliability directly affect profitability. When cooling fails in a data center or food processing facility, the consequences are immediate and costly. Heavy-duty industrial coolers with redundant components ensure continuous operation.
Compliance & Regulatory Requirements are non-negotiable in many industries. Whether storing food under HACCP guidelines or maintaining pharmaceuticals under GMP standards, your cooling system plays a crucial role in meeting these requirements.
Waste Reduction comes from proper cooling. Reliable industrial coolers extend product shelf life, prevent manufacturing defects, and reduce energy waste—contributing to sustainability goals and cost savings.
For more insights on finding the perfect cooling solution, our article on how to choose the perfect commercial cooler offers practical guidance.
Selecting the Right Industrial Cooler for Your Needs
Finding the perfect industrial cooler means identifying where performance meets practicality and budget requirements.
Key Factors to Consider
Your industrial cooler must handle your specific heat load (BTU/hr or tons of refrigeration), accounting for products being cooled and heat-generating equipment inside the space.
Location matters significantly. The humid Southeast challenges air-cooled systems during summer, while water-conscious Southwest regions might benefit from dry or adiabatic systems. Northeast and Midwest installations require freeze protection for water-cooled systems.
Space constraints often limit options. Air-cooled industrial coolers need more room than water-cooled systems with the same capacity. Walk-ins require adequate ceiling clearance and floor space.
Available utilities guide your decision:
- Water availability, quality, and cost
- Electrical service capacity
- Drainage systems
- Natural gas availability for absorption systems
Budget considerations include:
- Initial equipment cost
- Installation expenses (20-50% of equipment cost)
- Long-term energy consumption
- Water usage and treatment costs
- Maintenance requirements
- Expected system lifespan (15-20 years for quality systems)
Sustainability features in modern industrial coolers include energy-efficient designs, low-GWP refrigerants, water conservation technologies, and heat recovery options.
Key Features & Specifications to Evaluate
Construction materials affect longevity and performance. Copper tubes with aluminum fins provide excellent heat transfer and corrosion resistance. Stainless steel offers superior durability in harsh environments.
For walk-in coolers, look for 4" thick insulation exceeding EISA energy standards, aluminum T-rail flooring, and cam-action locking devices with heavy-duty gaskets.
Motor efficiency matters:
- Motors from 3/4 to 10 HP depending on needs
- High-efficiency designs meeting E.I.S.A. standards
- Variable-speed options for precise control
- Specialized motors for hazardous environments
Modern control systems transform industrial cooler operation. Basic thermostatic controls work for simple applications, but programmable controllers with data logging provide optimization insights. Remote monitoring allows system checking from anywhere.
Modularity supports future expansion. Look for modular wet sections for customizable cooling performance and walk-in coolers designed for easy expansion.
Insulation performance impacts energy efficiency. Quality walk-in coolers feature R-29 for cooler panels and R-32 for freezer panels.
For more on walk-in cooler features and costs, see our guide on walk-in cooler features and prices.
Energy Efficiency & Environmental Considerations
All new walk-in coolers must comply with Energy Independence and Security Act (EISA) standards, setting minimum requirements for insulation, motor efficiency, and system performance.
The industry continues shifting away from high Global Warming Potential (GWP) refrigerants. Hydrocarbon refrigerants offer excellent efficiency with minimal environmental impact.
"Free cooling" can reduce energy bills in cooler climates. Dry coolers can provide process cooling without running compressors when outside temperatures drop, sometimes reducing cooling costs by 70% during winter.
Heat recovery systems capture waste heat for useful purposes like heating water or warming workspace during winter.
Water usage matters as drought affects more regions. Closed-loop fluid coolers recycle cooling water, while adiabatic coolers like those from Ripley Engineering use minimal water while maintaining efficiency.
Cost Breakdown: CapEx vs OpEx
Initial investment (CapEx) includes equipment purchase—starting around $7,956.87 for a basic 10×10 walk-in cooler. Installation typically adds 20-50% to that figure.
Operating expenses (OpEx) often exceed the initial purchase price over the system's lifetime, including energy consumption, water costs, maintenance, and component replacements.
When calculating ROI, consider energy savings, productivity improvements, product quality benefits, maintenance costs, and expected useful life.
Available incentives can improve ROI, including utility rebates, tax incentives, accelerated depreciation, and custom incentives for large projects.
For tight budgets, see our article on walk-in coolers that won't freeze your budget.
Installation, Maintenance & Safety Best Practices for Industrial Coolers
Installation Guidelines
Proper site preparation is essential for industrial cooler installation. Allocate space for the unit plus clearances for airflow and maintenance access. Ensure the foundation can support the unit's weight, and verify electrical service, water connections, and drainage systems are ready.
Consider noise impact when positioning units, keeping them away from quiet work areas or neighboring properties.
Professional commissioning includes testing all components, verifying operating parameters match design specifications, and calibrating the control system. Operator training ensures your team can run the equipment correctly.
Preventive Maintenance
Regular maintenance extends industrial cooler life and maintains efficiency. Cleaning heat exchanger fins with appropriate tools removes dirt that impacts cooling efficiency. For water-cooled systems, proper water treatment prevents scale and biological growth.
Create a maintenance calendar with daily visual checks, weekly operational verification, and monthly/quarterly inspections. The small investment in regular maintenance pays dividends in equipment longevity and performance.
Safety Considerations
Safety around industrial coolers is essential. Wear appropriate PPE when working on cooling systems, including chemical/temperature-resistant gloves, eye protection, and possibly hearing protection in noisy mechanical rooms.
Lock-out/tag-out procedures save lives. Before maintenance, isolate electrical power, verify zero-energy state, and secure lockout devices. Clear communication prevents accidental start-ups.
For refrigerant systems, proper handling requires EPA certification. Regular leak detection should be part of your maintenance routine, and have an emergency response plan ready for significant refrigerant releases.
Common Challenges & Troubleshooting Tips
High head pressure often indicates a dirty condenser, failed fan, or refrigerant overcharge. Check for blocked airflow around the condenser and clean visible debris. Ice buildup may indicate defrost cycle issues, door seal air leaks, or incorrect refrigerant charge.
Scale formation in water-cooled systems reduces efficiency before visible damage occurs. Regular water quality testing helps catch problems early.
Strange noises and vibrations usually indicate mechanical issues like unbalanced fans, loose hardware, or worn bearings. Address these warning signs promptly.
When professional help is needed, our guide on finding walk-in cooler repair fast can help locate qualified service providers.
Maintenance Checklists
A structured maintenance routine extends industrial cooler life while maintaining performance. Daily checks include temperature verification, listening for unusual noises, and checking condensate drainage.
Monthly tasks include cleaning/replacing air filters, checking belt tension, inspecting electrical connections, and testing safety controls.
Annual maintenance should include thorough coil cleaning, refrigerant system inspection, control calibration, and electrical system testing. Compare current performance readings against baseline data to identify efficiency trends.
Modern industrial coolers increasingly incorporate IoT sensors providing real-time performance data, predictive analytics identifying potential failures, and remote monitoring capabilities.
Maintain detailed logs of all work performed, temperature readings, energy consumption, and repair history for troubleshooting and equipment replacement planning.
Future Trends & Innovations in Industrial Coolers
Smart Controls & Connectivity
Today's cutting-edge industrial coolers feature cloud connectivity allowing facility managers to monitor performance remotely. These smart systems can automatically adjust operation to maximize efficiency based on current conditions and integrate with building management systems.
Variable-Speed Technology
Variable-speed components allow industrial coolers to run at precisely the speed needed for current conditions. EC (electronically commutated) fan motors, variable-speed compressors, and intelligent pump controls match output exactly to cooling load, resulting in lower energy bills, reduced component wear, and more consistent temperatures.
IoT Diagnostics
IoT sensors throughout industrial cooler systems monitor health in real-time, tracking temperature, pressure, vibration patterns, and energy consumption. When parameters drift outside normal ranges, the system alerts maintenance staff immediately. Historical performance data helps identify optimization opportunities.
Hybrid Adiabatic Systems
Hybrid adiabatic industrial coolers operate as dry coolers most of the time, using no water during moderate weather. When temperatures climb, they activate evaporative cooling capabilities to maintain performance without massive energy consumption, using water only when necessary.
Low-GWP Refrigerants
Environmental regulations are driving changes in refrigerant technology. Natural refrigerants like CO2, ammonia, and hydrocarbons offer excellent cooling with minimal environmental impact. HFO (hydrofluoroolefin) blends provide transitional options with lower GWP than traditional HFCs.
Additive Manufacturing Impact
3D printing enables complex geometries in industrial cooler components that would be impossible with traditional manufacturing. For heat exchangers, this means optimized designs maximizing heat transfer while minimizing material use and pressure drop.
Modular Plug-and-Play Units
Modular industrial coolers feature standardized connection points that reduce installation time and complexity. Need more cooling capacity? Simply add another module rather than replacing the entire system. This approach also simplifies maintenance, as individual modules can often be serviced without shutting down the entire system.
Emerging Energy-Smart Industrial Coolers
AI-powered control systems learn from experience, analyzing patterns and automatically adjusting operation to minimize energy use while maintaining ideal conditions. They can predict maintenance needs and compensate for aging components.
Demand-response capabilities allow industrial coolers to communicate with utility companies and reduce consumption during grid stress periods, earning financial incentives. Some systems pre-cool spaces when electricity rates are lower.
Solar-assisted cooling integrates photovoltaic panels or solar thermal collectors with cooling systems to reduce grid electricity consumption. When paired with battery storage, they can provide cooling during power outages.
Microchannel heat exchangers feature numerous small parallel channels rather than traditional tube designs, improving heat transfer efficiency while reducing refrigerant charge requirements by up to 70%.
Sustainability Certifications & Regulatory Outlook
The Department of Energy's 2027 rules will significantly raise efficiency standards for industrial coolers. These new requirements will improve insulation performance and component efficiency.
ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) reporting is influencing cooling system decisions as companies document sustainability efforts.
Refrigerant regulations continue tightening globally, with phase-down schedules for high-GWP substances accelerating under the AIM Act and Kigali Amendment. Facilities using older refrigerants should plan for transitioning to lower-GWP alternatives.
Water usage in cooling systems faces increased regulation, with once-through cooling systems being restricted and water quality discharge requirements tightening. Water-efficient industrial coolers provide insurance against these regulatory risks.
Frequently Asked Questions about Industrial Coolers
What size industrial cooler do I need for my process?
Determining the right size for your industrial cooler requires calculating your total heat load, including process heat load (BTU/hr or tons of refrigeration), ambient heat gain, infiltration load, and internal loads from lights, equipment, and people.
For walk-in coolers, standard sizes include 6×6×8, 6×8×8, 8×8×8, and 8×10×8 feet, with custom dimensions available for specific needs.
For process cooling applications, a professional heat load calculation is recommended to analyze your requirements and suggest a system with room for future growth.
How often should industrial coolers be serviced?
Maintenance frequency depends on system type, usage, and environment. Daily visual checks for leaks, temperature verification, and condensate drainage will catch many issues early.
Monthly maintenance should include cleaning/replacing air filters, checking belt tension, inspecting electrical connections, and cleaning external surfaces.
Quarterly maintenance involves comprehensive coil cleaning, checking refrigerant levels, testing control systems, and inspecting water treatment for water-cooled systems.
Annual professional inspection should include refrigeration system maintenance, control calibration, performance verification, and safety device testing.
For mission-critical cooling (like in mortuary settings), more frequent service intervals are recommended.
Are evaporative or adiabatic coolers suitable for humid climates?
Evaporative and adiabatic industrial coolers have limited effectiveness in humid climates since they rely on water evaporation for cooling.
Evaporative coolers work best in dry climates (below 30% humidity). They're still effective at medium humidity (30-50%), but performance drops significantly above 60% humidity because the air is already moisture-laden.
Adiabatic coolers are more versatile, switching to dry mode during humid conditions and using evaporative pre-cooling only when beneficial. They adapt to weather conditions, providing more consistent performance across varying humidity levels.
In humid climates, consider:
- Hybrid systems switching between evaporative and dry operation
- Oversized evaporative media to maximize cooling effect
- Supplemental mechanical cooling for high humidity periods
- System design accounting for local climate conditions
For locations with seasonal humidity changes, adiabatic coolers often offer the best compromise, operating in water-saving dry mode during humid summer months and using evaporative cooling when conditions are favorable.
Conclusion
Choosing the right industrial cooler requires matching cooling technology to your specific application. Walk-in coolers excel at large-scale cold storage, fluid coolers provide process cooling efficiency, evaporative systems can reduce energy costs by up to 70% in suitable climates, and spot coolers deliver targeted cooling for specific areas.
Look beyond the initial price to consider total cost of ownership, including energy consumption, water usage, maintenance requirements, and equipment lifespan. Sometimes paying more upfront for efficiency features saves thousands in the long run.
Modern cooling systems incorporate energy-saving technologies, environmentally-friendly refrigerants, and smart controls that reduce both carbon footprint and utility bills. Regular maintenance extends equipment life and maintains peak performance, often paying for itself by preventing costly emergency repairs.
Stay aware of evolving regulations, as efficiency standards continue to tighten and refrigerant regulations evolve rapidly. Choosing forward-thinking technology now can prevent compliance headaches later.
At American Mortuary Coolers, we understand that cooling supports the important work you do. Based in Tennessee, we specialize in crafting custom cooling solutions for sensitive applications such as funeral services. We deliver our durable, custom industrial coolers directly to customers across all 48 contiguous states, from small towns to major cities like New York, Los Angeles, Dallas, and everywhere in between.
Our experienced team helps you find the perfect cooling solution for your specific situation, whether you're cooling a production process, storing temperature-sensitive products, or maintaining a respectful environment for mortuary services.
For more information about our custom mortuary cooling solutions, visit American Mortuary Coolers—your one-stop shop for mortuary coolers.
Making an informed decision about your industrial cooler today ensures efficient, reliable cooling for years to come, supporting your operational goals while minimizing environmental impact and operating costs.




