
Everything You Need to Know About Reefer Trucks
Why Reefer Trucks Are the Backbone of America's Cold Chain
A reefer truck is a specialized vehicle equipped with its own refrigeration system to transport temperature-sensitive goods like food, pharmaceuticals, and other perishables. Here's what makes them essential:
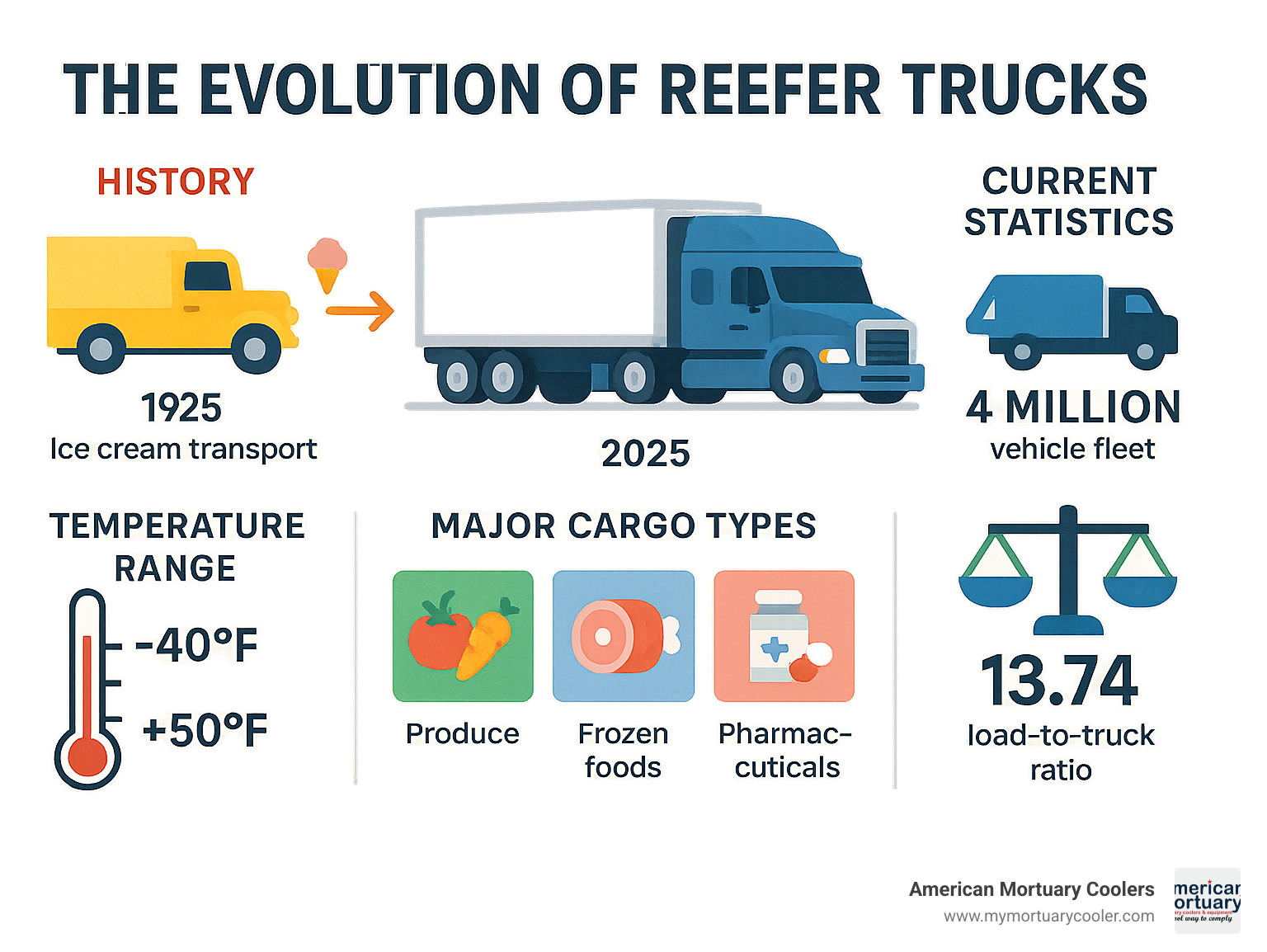
- Temperature Range: Can maintain cargo temperatures as low as -40°F
- Fuel System: Separate 50-gallon diesel tank powers the refrigeration unit
- Cargo Types: Fresh produce, frozen foods, pharmaceuticals, flowers, and medical supplies
- Market Demand: Reefer load-to-truck ratios are nearly double that of dry van loads (13.74 vs 7.33)
- Fleet Size: Over 4 million refrigerated vehicles operate worldwide
The story of refrigerated transport began in 1925 when American inventor Frederick McKinley Jones created the first mechanical refrigeration system for trucks. What started as a solution for the ice cream industry has grown into a critical part of our food supply chain.
Today's reefer trucks serve as mobile cold storage units, ensuring that fresh food and life-saving medications arrive in perfect condition. With reefer freight rates averaging $3.04 per mile - significantly higher than standard dry freight - these specialized vehicles offer both essential service and strong profit potential.
What Is a Reefer Truck and Why Does It Matter?
Think of a reefer truck as a mobile freezer or refrigerator on wheels. The name comes from "refrigerated," and these specialized vehicles are equipped with their own active cooling systems - not just basic insulation like you'd find on a regular truck.
While a standard dry van simply protects your cargo from rain and road debris, a reefer truck actively controls the temperature inside its insulated box. It's the difference between storing your groceries in a cardboard box versus keeping them in your kitchen refrigerator.
This active cooling capability is essential for countless goods that could spoil, lose their effectiveness, or even become dangerous if they get too warm or too cold. With over 4 million refrigerated vehicles operating worldwide, and reefer load-to-truck ratios nearly double those of standard dry vans, these specialized trucks stay busy around the clock.
| Feature | Reefer Truck | Dry Van |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature Control | Active cooling/heating system | No temperature control |
| Insulation | Heavy-duty insulated walls | Basic weather protection |
| Power Source | Separate diesel generator | None |
| Cargo Types | Temperature-sensitive goods | General freight |
| Freight Rates | $3.04/mile average | Lower rates |
| Fuel Consumption | Higher (refrigeration unit) | Standard |
Reefer Truck vs. Reefer Trailer
A reefer straight truck is all one piece - the cab and the refrigerated box are permanently attached. These range from smaller Class 1 vehicles (under 6,000 pounds) perfect for local deliveries, all the way up to Class 8 trucks (over 33,000 pounds) that can handle serious cargo loads. The advantage? You can steer tight city streets and back into loading docks that would challenge a semi-trailer driver.
A reefer trailer is that massive 53-foot refrigerated box you see attached to semi-trucks on the interstate. These are the heavy hitters of long-haul refrigerated transport, capable of carrying between 43,000 and 45,000 pounds of cargo across the country.
The choice often comes down to where you're going and what CDL class your drivers have. Local routes with frequent stops? The straight truck wins. Cross-country hauls with maximum cargo? That's trailer territory.
Key Cargo Types Moved by a Reefer Truck
Reefer trucks transport goods that touch nearly every aspect of our lives. Fresh produce like lettuce and bananas actually generate their own heat as they ripen, so they need continuous cooling. Dairy products - your milk, cheese, and yogurt - require consistent refrigeration from farm to store. Meat and seafood need precise temperature control whether frozen or kept just above freezing.
Pharmaceuticals including vaccines and insulin depend on reefer transport to maintain their life-saving properties. Fresh flowers for weddings would wilt without climate control. Even electronics can be damaged by extreme temperatures, and cosmetics can separate or spoil in heat - so they often ride in temperature-controlled trucks too.
How Does a Reefer Truck Work?
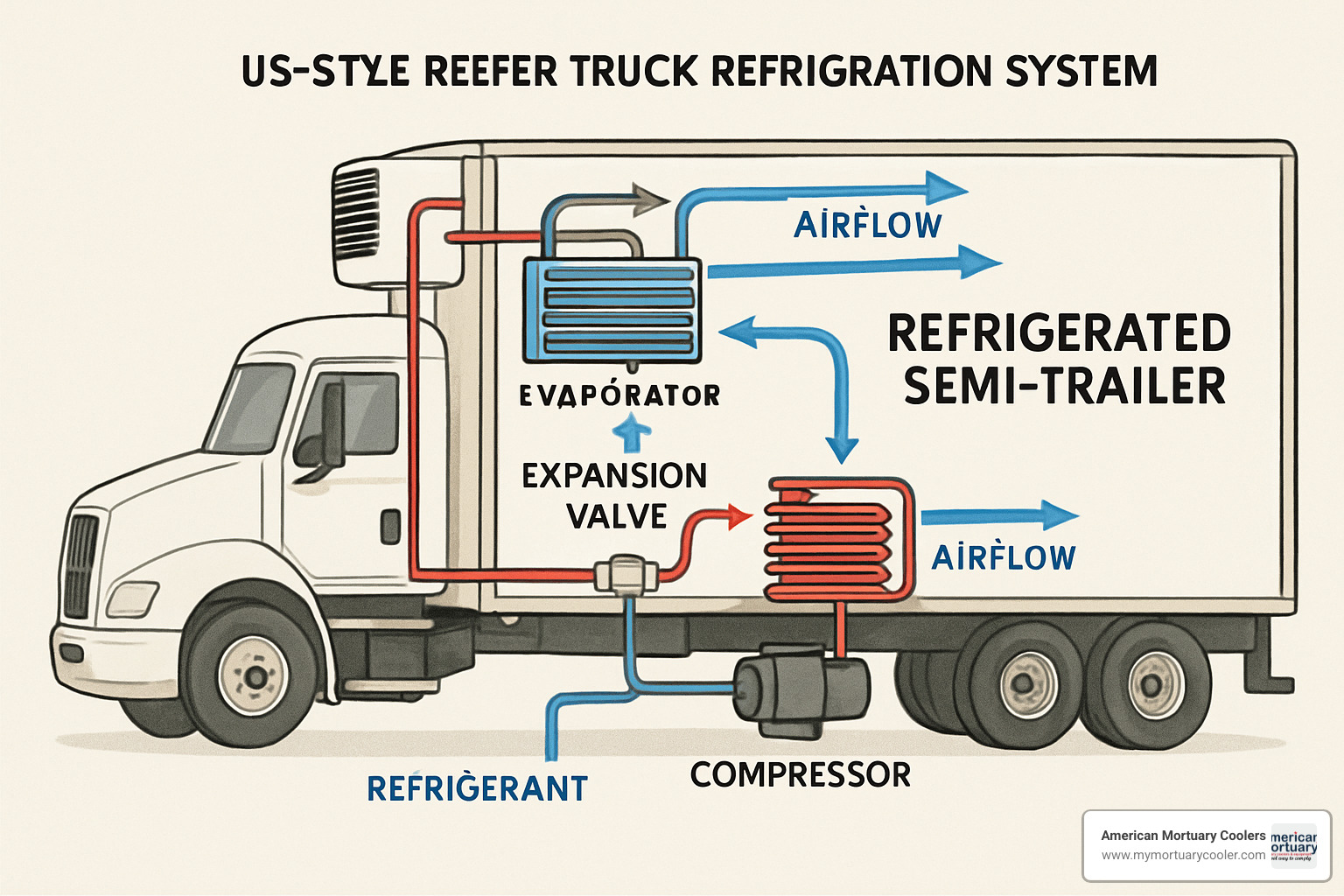
Think of a reefer truck as a giant refrigerator on wheels. The magic happens through a closed-loop refrigeration system that works around the clock to maintain precise temperatures.
The process starts with the compressor, powered by its own small diesel engine. This compressor pressurizes refrigerant and pushes it through the system. The condenser acts like a radiator, removing heat from that pressurized refrigerant. The expansion valve regulates how much refrigerant flows through. Finally, the evaporator absorbs heat from inside the trailer and creates the cold air that keeps your cargo fresh.
Most modern reefer units give you two operating choices. Continuous mode keeps the air flowing constantly, perfect for fresh produce that generates its own heat. Cycle mode runs intermittently to save fuel and works great for frozen goods that don't create heat.
Some cutting-edge systems use cryogenic cooling with liquid carbon dioxide or nitrogen. These systems are whisper-quiet and can reach extremely low temperatures.
Reefer Truck Components Explained
The insulated walls aren't just thick - they're engineered with dense foam insulation sandwiched between metal or fiberglass panels, creating an airtight environment that locks in the cold.
The T-floor design allows cold air to flow underneath pallets and cargo, ensuring even the boxes at the bottom stay properly chilled. The air chute system runs along the ceiling, distributing frigid air from the refrigeration unit all the way to the back of the trailer.
That separate 50-gallon fuel tank means the refrigeration system runs independently of the truck's main engine. Your cargo stays cold even when the truck is parked for loading, unloading, or during mandatory rest breaks.
Modern reefer units are packed with sensors and telematics that monitor temperature, humidity, and performance in real-time, sending alerts if anything goes wrong.
For a deeper dive into refrigeration principles, check out our Comprehensive Guide to Refrigeration Units and How They Work.
Temperature Control & Monitoring
Temperature control in a reefer truck uses multiple sensors throughout the cargo area, ensuring consistent temperatures from front to back and top to bottom.
Data loggers record every temperature reading throughout the journey, creating a detailed record that's essential for regulatory compliance under FSMA compliance rules.
GPS-enabled monitoring allows fleet managers to track both location and temperature remotely, receiving instant alerts if temperatures drift outside acceptable ranges. Remote alerts can save thousands of dollars in spoiled cargo by notifying operators immediately of any problems.
For detailed regulatory requirements, the FDA provides comprehensive sanitation guidelines that cover temperature-controlled transport requirements.
Sizes, Capacities, Makes & Money

Shopping for a reefer truck is like choosing the right tool for the job. With over 2,900 reefer truck listings currently for sale across the U.S., you'll find everything from compact delivery vehicles to massive highway haulers.
The truck classification system runs from Class 1 vehicles under 6,000 pounds all the way up to Class 8 heavy-duty trucks over 33,000 pounds. When it comes to trailer dimensions, you're looking at lengths from 28 to 53 feet, with the standard over-the-road reefer measuring 53 feet long, 8 feet 6 inches wide, and 13 feet 6 inches tall.
Maximum payload capacity ranges from 43,000 to 45,000 pounds for standard reefer trailers. That number gets reduced by about 2,000 pounds for the refrigeration unit itself, but you're still hauling serious weight.
The big names in reefer manufacturing include Great Dane, Utility's 3000R series, and Hyundai Translead's ThermoTech series. Purchase prices range widely - you can find used reefer trucks starting around $10,000 for older, smaller units, while new large-capacity trailers can run $120,000 or more. Companies like Penske offer rental options with some of the newest refrigerated truck fleets.
Cost Breakdown & ROI
Operating a reefer truck costs more than a standard dry van, but the math often works in your favor. Your annual operating costs will include about $4,000 in reefer fuel and $1,500 in specialized maintenance on top of regular trucking expenses. However, reefer loads average $3.04 per mile compared to lower rates for dry freight.
The demand story gets even better. Reefer loads show a load-to-truck ratio of 13.74 compared to just 7.33 for dry vans. This means less time waiting for loads and more time making money.
Insurance gets more complex with reefers. You'll need specialized reefer endorsements and higher coverage limits for temperature-sensitive cargo. Cargo spoilage coverage is essential because a single breakdown can wipe out tens of thousands of dollars worth of product.
Reefer Truck Maintenance Checklist
Keeping your reefer truck running smoothly means staying on top of both the vehicle and the refrigeration system. Your pre-trip inspection needs to include checking refrigerant levels, testing the defrost cycle, and ensuring temperature sensors work correctly.
The refrigeration unit demands annual professional service that includes refrigerant leak testing, compressor inspection, and thorough cleaning of the condenser coils. The air chute system needs regular cleaning to maintain proper airflow.
Sanitizing the trailer after each load isn't just good practice - it's required for food safety compliance. This means thorough washing with approved chemicals, followed by complete drying to prevent mold and bacteria growth.
A well-maintained reefer truck can last 8 years or more with under 4,000 annual operating hours. That makes proper care one of the smartest investments you can make.
For more insights on maintaining refrigeration equipment, our guide on Reliable Refrigeration Storage provides valuable maintenance tips that apply across different types of refrigerated systems.
Benefits, Risks, and Regulations
Running a reefer truck business comes with attractive perks and significant challenges. The biggest draw? Higher freight rates that make the extra investment worthwhile. Reefer loads command premium pricing - often 20-30% more per mile than dry van loads.
There's also the recession-proof nature of this business. People need food, medicine, and other essentials regardless of economic conditions. Another bonus is reduced deadhead miles - your reefer trailer can haul dry freight when you don't need refrigeration.
But the risks are real. Temperature failures are every reefer operator's nightmare. One breakdown can mean total cargo loss - tens of thousands of dollars down the drain. Strict delivery schedules add pressure too. When you're hauling fresh produce or pharmaceuticals, there's no wiggle room for delays.
The regulatory landscape adds complexity. The Food Safety Modernization Act (FSMA) requires detailed temperature records and strict sanitation procedures. FDA regulations govern food transport, while CARB emissions regulations in California push the industry toward cleaner technologies.
Insurance considerations are crucial. You'll need specialized reefer endorsements and higher coverage limits for temperature-sensitive cargo. Cargo spoilage coverage is essential - without it, one system failure could bankrupt your operation.
Cleaning & Sanitation Standards
Keeping your reefer truck clean isn't just about looking professional - it's often the law. FDA guidelines require specific washout procedures using approved chemicals to eliminate bacteria, mold, and odors that can contaminate future loads.
The cleaning process involves removing all debris, washing with hot water and approved detergents, sanitizing with chemical solutions, and completely drying the trailer. Documentation is everything - many shippers require proof of cleaning.
The technology behind reefer trucks has found unexpected applications beyond normal freight transport. Our article on Refrigerated Trucks as Morgues: A Chilling Look at Emergency Solutions explores how these vehicles serve critical roles in emergency situations.
Insurance & Liability Considerations
Reefer truck operations need specialized insurance coverage beyond standard commercial trucking policies. Cargo spoilage coverage protects you when the refrigeration system fails, while reefer breakdown endorsements cover emergency repairs and alternative transportation costs.
Liability extends beyond cargo value to include food safety violations and potential health impacts from spoiled products. One contaminated load could lead to lawsuits and regulatory penalties that dwarf the original cargo value.
For detailed information on coverage options, protection for cargo liability offers comprehensive guidance on reefer insurance requirements and best practices.
Maximizing Fleet Profitability & Sustainability
Smart reefer truck operations focus on maximizing efficiency while minimizing costs. Load planning software helps identify opportunities to combine refrigerated and dry freight, reducing empty miles and increasing revenue per trip.
Minimizing empty miles is crucial for profitability. Reefer trailers can carry dry freight when refrigeration isn't needed, and strategic positioning near major shipping areas reduces deadhead time.
Automation plays an increasingly important role in fleet management. Telematics systems monitor fuel consumption, track maintenance schedules, and provide real-time temperature alerts. Driver training significantly impacts both safety and profitability through proper loading techniques and fuel-efficient driving practices.
Future Tech: Diesel vs. Cryogenic vs. Electric
The future of reefer truck technology is evolving rapidly. Traditional diesel-powered refrigeration units face increasing emissions regulations, driving innovation in alternative cooling methods.
Cryogenic systems using liquid carbon dioxide or nitrogen offer extremely low temperatures and zero emissions during operation. Electric refrigeration units, powered by batteries or hybrid systems, eliminate direct emissions and reduce noise levels significantly.
Zero-emission mandates in California and other states are accelerating adoption of these technologies. Federal and state grants often help offset the higher initial costs, improving the return on investment for early adopters.
Reefer Truck Maintenance Tech Stack
Modern reefer truck maintenance relies heavily on technology to predict problems before they cause breakdowns. Telematics systems monitor dozens of parameters in real-time, from refrigerant pressures to compressor performance.
Predictive analytics use this data to identify patterns that indicate impending failures, allowing preventive maintenance that costs less than emergency repairs. Electronic driver vehicle inspection reports (E-DVIR) ensure consistent documentation and help identify issues early.
For comprehensive information on commercial refrigeration repair and maintenance, our Complete Guide to Commercial Refrigeration Repair Near You provides detailed guidance on finding qualified service providers and maintaining optimal performance.
Frequently Asked Questions about Reefer Trucks
How cold can a reefer truck get?
When people ask about the coldest temperatures a reefer truck can reach, they're often surprised by the answer. Modern refrigeration units can maintain temperatures as low as -20°F to -40°F, which is cold enough to keep ice cream rock-solid during a cross-country haul or preserve temperature-sensitive pharmaceuticals that could lose their effectiveness if they warm up even slightly.
The exact temperature range depends on your specific refrigeration unit and the quality of the trailer's insulation. Most units are incredibly versatile - they can maintain any temperature from well below freezing up to about 50°F for heated cargo. This flexibility means the same truck that delivers frozen seafood in the morning can transport fresh flowers that afternoon.
What's the difference between continuous and cycle mode?
Understanding when to use continuous versus cycle mode can save you serious money on fuel while keeping your cargo in perfect condition. It all comes down to what you're hauling and how much heat it generates.
Continuous mode keeps the refrigeration unit running constantly, maintaining steady airflow and rock-solid temperatures. This is your go-to setting for fresh produce like lettuce or strawberries that actually generate their own heat as they ripen. These living products need that constant cooling to stay fresh.
Cycle mode is the fuel-saver option that runs the refrigeration unit intermittently. It works perfectly for frozen goods like ice cream or frozen vegetables that don't generate heat and can handle minor temperature fluctuations without any quality loss. The savings on diesel fuel can really add up over long hauls.
Do I need special fuel for the reefer unit?
Yes, and this is one detail that catches new operators off guard. Reefer trucks typically use red-dyed diesel fuel, which is different from the regular diesel in your truck's main tank. This red fuel is untaxed because it's not used for highway travel - it only powers the refrigeration unit.
The reefer unit has its own separate 50-gallon tank dedicated just to running the cooling system. Using this untaxed red diesel instead of regular highway diesel can result in significant cost savings over time. Just remember - it's illegal to use this red-dyed fuel in your truck's main engine, so keep those fuel systems separate.
This setup means your refrigeration can keep running even when your truck is parked for loading, unloading, or mandatory rest periods. That's crucial for maintaining the cold chain and protecting your valuable cargo.
Conclusion
The journey of reefer trucks from Frederick McKinley Jones's 1925 ice cream innovation to today's 4-million-vehicle global fleet tells a remarkable story of American ingenuity. These mobile cold storage units have become the unsung heroes of our daily lives, ensuring that everything from your morning yogurt to life-saving medications arrives exactly as intended.
Success in the reefer business isn't just about buying a truck with a cooling unit. It's about mastering the balance between higher operating costs and premium freight rates, understanding that your $4,000 annual reefer fuel bill is an investment that pays dividends through $3.04-per-mile rates and a load-to-truck ratio nearly double that of dry freight.
The best operators know that rigorous temperature control goes far beyond setting a thermostat. They understand FSMA compliance, maintain detailed temperature logs, and treat their monitoring systems as critical business tools.
At American Mortuary Coolers, we've spent years working with specialized temperature-controlled equipment across Tennessee and the contiguous 48 states. Our experience crafting custom solutions has taught us that reliable refrigeration - whether mobile or stationary - requires the same fundamental principles: quality components, proper maintenance, and attention to detail.
The technology landscape continues evolving rapidly. Electric reefer units and cryogenic systems are challenging traditional diesel-powered refrigeration, driven by zero-emission mandates and environmental concerns. Solar-assisted units and predictive maintenance technology are reshaping how operators think about efficiency and uptime.
For those considering stationary cold storage solutions to complement their mobile operations, our Ultimate Guide to Walk-In Fridge and Freezer Combos explores how permanent refrigeration systems can improve your cold chain capabilities.
The future looks bright for reefer truck operations. With recession-proof demand for essential goods, advancing technology that improves efficiency, and growing awareness of food safety requirements, opportunities abound for operators who commit to excellence.
Whether you're hauling fresh strawberries from California farms or transporting temperature-sensitive pharmaceuticals to rural hospitals, you're doing more than moving freight. You're maintaining the cold chain that modern life depends on - and that's a responsibility worth taking seriously.
Ready to explore custom cold-storage solutions for your operations? We're here to help you find the right temperature-controlled equipment to keep your business running smoothly.



